AI-Powered Home Security guide
AI-powered home security can sharpen alerts, reduce false alarms, and make monitoring simpler for households across the UK. From doorbells that recognise common events to cameras that record only when something happens, the latest systems blend convenience with careful data handling. This guide explains how the technology works, what features matter, and how to protect privacy.
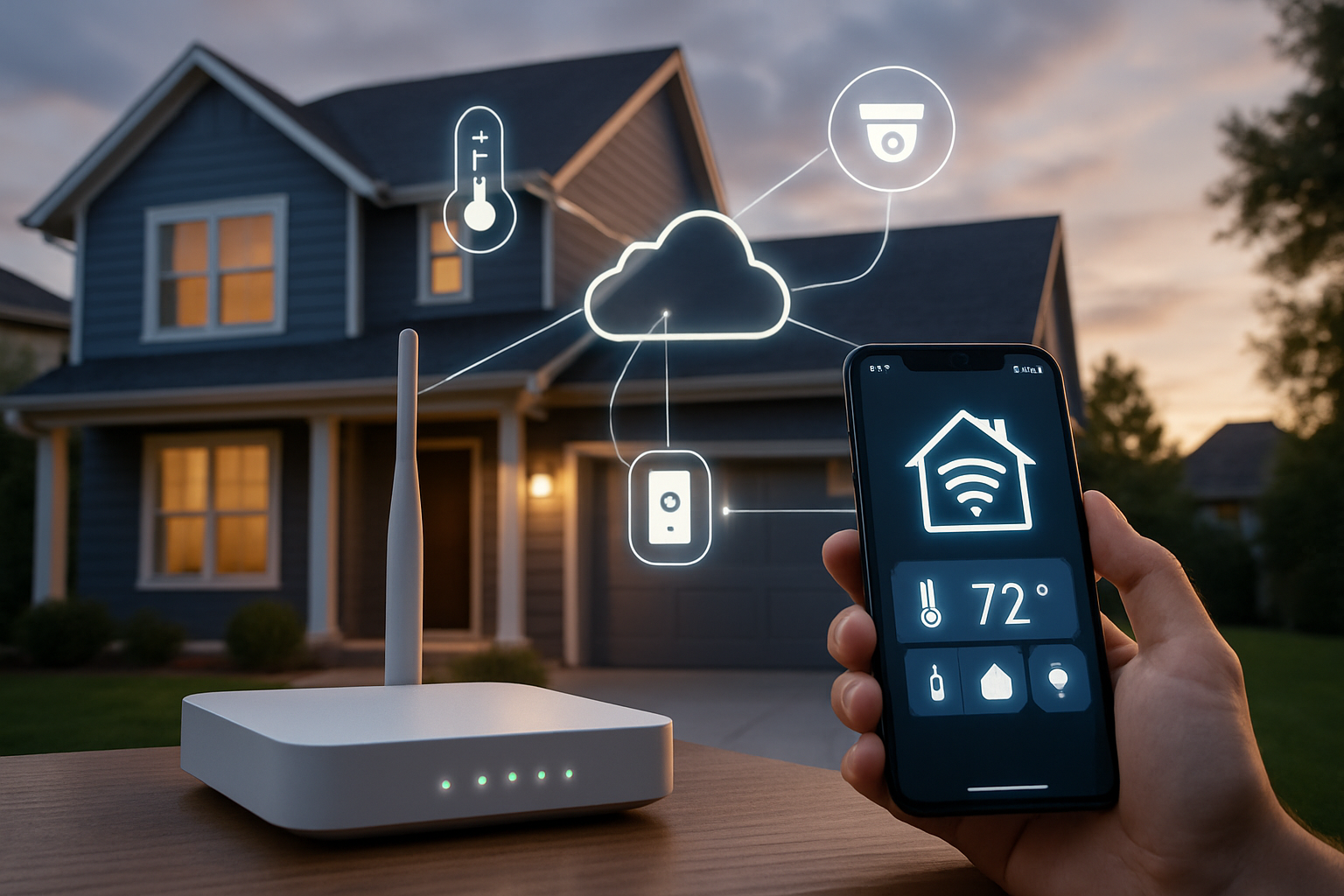

Artificial intelligence is reshaping how homes are protected in the UK, helping systems spot important events, filter noise, and respond faster. Rather than constant recording or motion alerts for swaying trees, modern kits use models that identify people, vehicles, animals, and packages, sending clearer notifications to your phone. The right setup can integrate with alarms, lights, and smart assistants, but it must also respect household routines, neighbours, and UK data rules. This guide breaks down core ideas, useful features, buying considerations, and responsible use.
Understanding AI in Home Security
AI in home security typically combines computer vision with pattern analysis to understand what is happening in view of a camera or sensor. On-camera or edge processing can classify events locally, while some systems use cloud inference for heavier tasks. This enables person detection rather than generic motion, event-based recording to save storage, and smarter alerts that arrive when something meaningful occurs.
Crucially, AI is not perfect. Models can misclassify unfamiliar objects, struggle in extreme weather, or falter with glare and low light. Reliability improves with good camera placement, adequate lighting, and periodic firmware updates. Many households mix video doorbells for the front entrance, floodlight cameras for driveways or gardens, and indoor units to protect entry points. Used together, these tools help distinguish routine comings and goings from incidents that warrant attention.
Key Features of AI-Powered Security Systems
When comparing capabilities, start with event detection. Person, vehicle, animal, and package detection reduce noise and help prioritise alerts. Activity zones and privacy masks limit what the camera monitors, which is useful near pavements or shared spaces. Pet-friendly motion profiles reduce false alarms from cats or dogs indoors.
Consider image quality that supports the AI: a wide dynamic range helps with backlit doorways, while colour night vision or well-placed lighting improves recognition after dark. Two-way talk, sirens, and light triggers can deter opportunistic behaviour. For resilience, look for local storage options, secure cloud backups, end-to-end encryption in transit and at rest, and two-factor authentication for accounts. Administrative controls such as user roles, audit logs, and emergency access codes are helpful for multi-person households.
Choosing the Right AI Security System
Start with a map of your property. Flats may prioritise a doorbell and lobby coverage, while detached homes might need driveway, side access, and garden views. Check your Wi‑Fi strength or plan for wired power and data using PoE where feasible. Position cameras high enough to avoid tampering but low enough for clear faces at typical distances.
Compatibility matters. If you already have an alarm panel, sensors, or smart lighting, choose devices that integrate reliably rather than duplicating features. Decide between local recording, cloud services, or a hybrid model based on how you prefer to access and share clips. Confirm weather resistance ratings for outdoor units, and look for robust night performance. In the UK, think about long winter nights, rain, and potential condensation; good housings and maintenance make a difference. Finally, review vendor transparency on updates and security practices, and ensure there is accessible support in your area if you need installation help.
Addressing Privacy Concerns
In the UK, domestic users enjoy some flexibility when cameras capture images only within their own property boundary. If your system records public spaces or neighbouring property, data protection law can apply, including principles in the UK GDPR and the Data Protection Act 2018. Use privacy masks and activity zones to minimise capture beyond your boundary, and clearly inform visitors when recording is in place, for example with a visible sign.
Keep retention periods reasonable and disable audio recording if it is not necessary, as voices may add extra sensitivity. Maintain a secure setup with unique passwords and two-factor authentication. Regularly update firmware to patch vulnerabilities. If you do capture areas outside your boundary, you may be responsible for responding to subject access requests and demonstrating a lawful basis such as legitimate interests. Avoid sharing identifiable clips on social media; if the police request footage, provide it through appropriate channels rather than posting publicly. Take extra care with features such as face recognition, which may be unnecessary for most households and can introduce additional legal and ethical risks.
Conclusion: Embrace Smart Security Choices
AI-powered home security can make monitoring more accurate and less intrusive when configured well. Focus on features that solve real problems, like targeted detection, reliable night imagery, and secure storage. Place cameras thoughtfully, tune zones to reduce overspill, and review alerts to ensure they remain useful. By aligning technology choices with the layout of your property, everyday routines, and local expectations, you can achieve a balanced system that protects your home while respecting privacy and community norms.